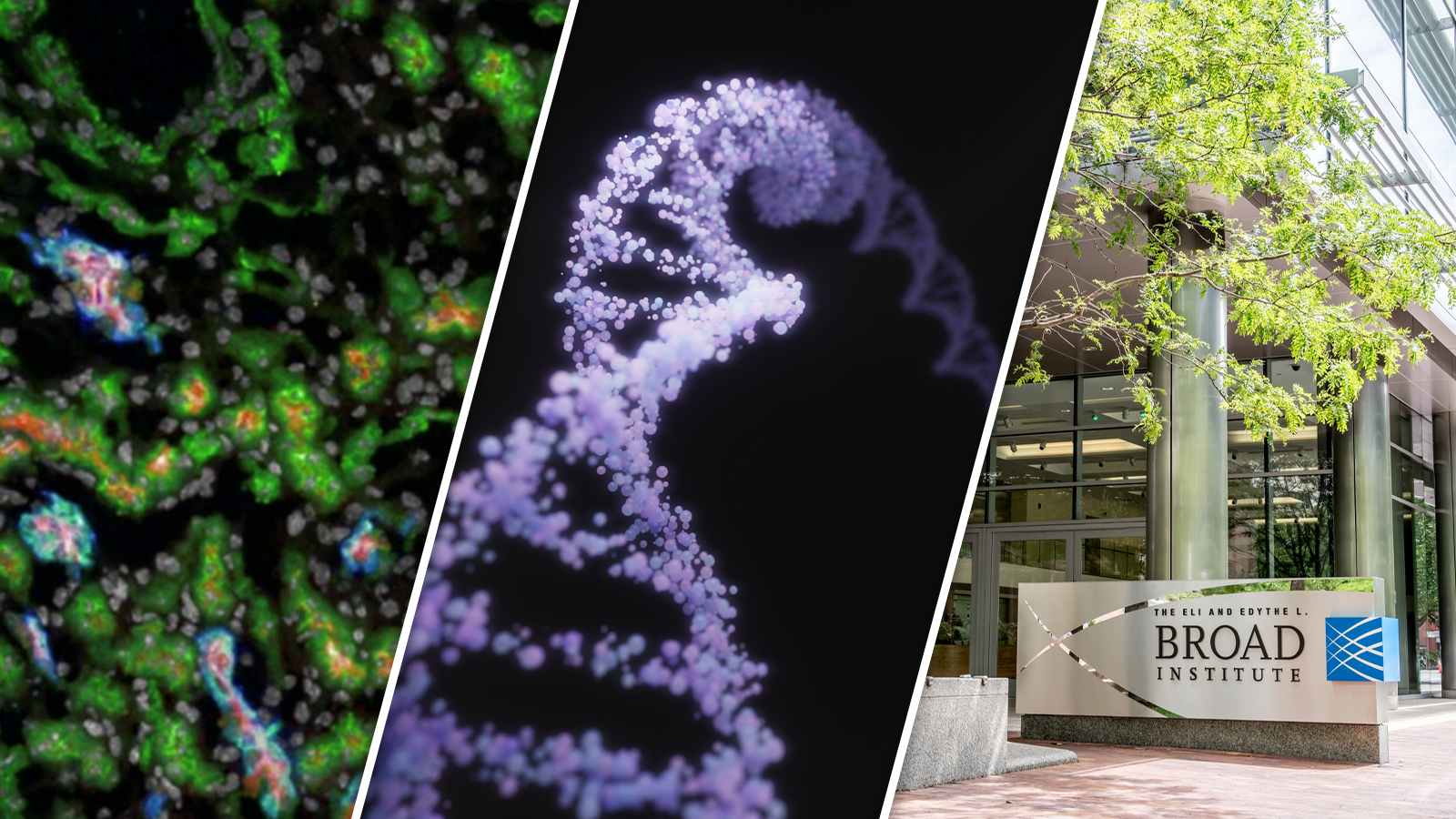
The future of next-generation sequencing is exciting. In the past year, a number of new businesses have entered the market, each with unique emerging platforms and cutting-edge technologies. As instruments – both new and old – computing platforms must adapt as well.
At GTC, NVIDIA announced its collaboration The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. The partnership will add NVIDIA’s AI and acceleration tools to Broad’s widely used genomic analysis platform, Terra. They claim that the outcome will offer faster analysis of more data.
“There’s a need across the healthcare ecosystem for better computational tools to enable breakthroughs in the way we understand disease, develop diagnostics and deliver treatments,” said Kimberly Powell, vice president of healthcare at NVIDIA. “By expanding our collaboration with the Broad Institute, we can bring the power of large language models to ultimately deliver joint solutions and narrow the divide between insights from researchers and real benefits for patients.”
Through the partnership, The Broad Institute aims to enable the next generation of collaborative biomedical research by providing an open cloud platform that connects researchers both to each other and to the datasets and tools they need to achieve scientific breakthroughs.
This collaboration also expands on a number of platforms that have already revolutionized scientists’ capacity to analyze genomic data.
“Life sciences are in the midst of a data revolution, and researchers are in critical need of a new approach to bring machine learning into biomedicine,” said Anthony Philippakis, chief data officer of the Broad Institute. “In this collaboration, we aim to expand our mission of data sharing and collaborative processes to scale genomics research.”
Specifically, the partnership has a focus on 3 areas:
- Making NVIDIA Clara Parabricks available in the Terra platform;
- Building large language models (LLMs);
- and Bringing improved deep learning to Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK).
Large Language Models to Study Disease
NVIDIA’s BioNeMo framework includes pretrained LLMs for proteins and chemistry that simplify training, inference and scaling. BioNeMo is an extension of the NVIDIA NeMo Megatron framework and is domain-specific for chemistry, proteins and DNA/RNA sequences.
BioNeMo allows developers to effectively train and deploy biology LLMs with billions of parameters. Together, teams from both organizations will build on this work, creating new models to add to the BioNeMo collection and make available in the Terra platform.
NVIDIA Software for Domain-Specific AI
NVIDIA Parabricks GPU-accelerated workflows provide researchers with faster turnaround times and lower costs for a wide range of genomic data analyses. For Broad’s GATK best practices germline workflow, doing the analysis with Parabricks on GPUs can be as much as 24x faster and less than half the cost.
Broad Institute researchers will also gain access to MONAI, an open-source deep learning framework for medical imaging AI, as well as NVIDIA RAPIDS™, a GPU-accelerated data science toolkit for faster data preparation, which can be used for genomic single-cell analysis.
Learn more about Clara Parabricks and Terra integration and sign up for early access to the NVIDIA BioNeMo LLM service.
Tune in to NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang’s GTC keynote to learn more about the collaboration with the Broad Institute.






