With NVIDIA Turing Architecture comes the release of NVIDIA GeForce RTX 20 series. NVIDIA GeForce RTX 20 series provides many new features, not just pure performance improvement from the previous generations of graphic cards. In this article, we will take a look at what the new Turing Architecture can do as compared to the previous generations.
More than just Ray-Tracing

Real-Time Ray Tracing may be the most hyped technology, but that is not the only thing that RTX can do. Together with the usual rasterization pipeline and compute units with CUDA, RTX brings about “Hybrid Rendering“. With “Hybrid Rendering“, many different types of frames can be rendered using either one or a combination of the available rendering technologies. Those frames can be further enhanced with DLSS.
Overview of Turing Architecture

The Tensor Core of the architecture can compute large matrix operations efficiently, allowing Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence to be possible with RTX. The main workload of the Real Time Ray Tracing is also handled by the RT Core. Beside these two main features, geometric shading pipeline is also available in the Turing Architecture. This will allow computationally heavy advanced shading to achieve a realistic scene.
Turing Memory Architecture
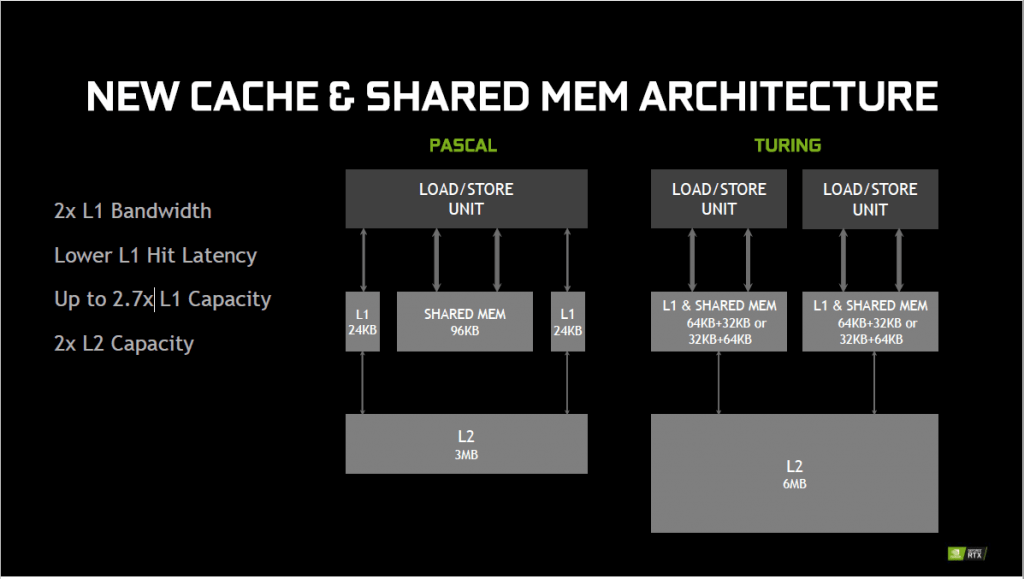
To support the new architecture, new cache and shared memory architecture is implemented as well. The new memory architecture has twice the amount of L1 bandwidth and L2 capacity as compared to the memory found in the pascal architecture. With this new architecture, the shading performance with Turing architecture is 50% better than with Pascal architecture. The Turing architecture also comes with GDDR6, which has the fastest memory interface of up to 14 Gbps and 40% lower Crosstalk.
Real-Time Ray Tracing
Ray Tracing is a rendering technique that have been around in the world of computing for a very long time. It allows for an accurate lighting to be render on object surfaces which results in a more realistic object. However, this is a very computationally complex and tedious rendering technique, and real time ray traced scenes with high frame rate is not feasible until recently. NVIDIA RTX is able to achieve real-time ray tracing through the use of Bounding Volume Hierarchy algorithm as well as RT Cores.
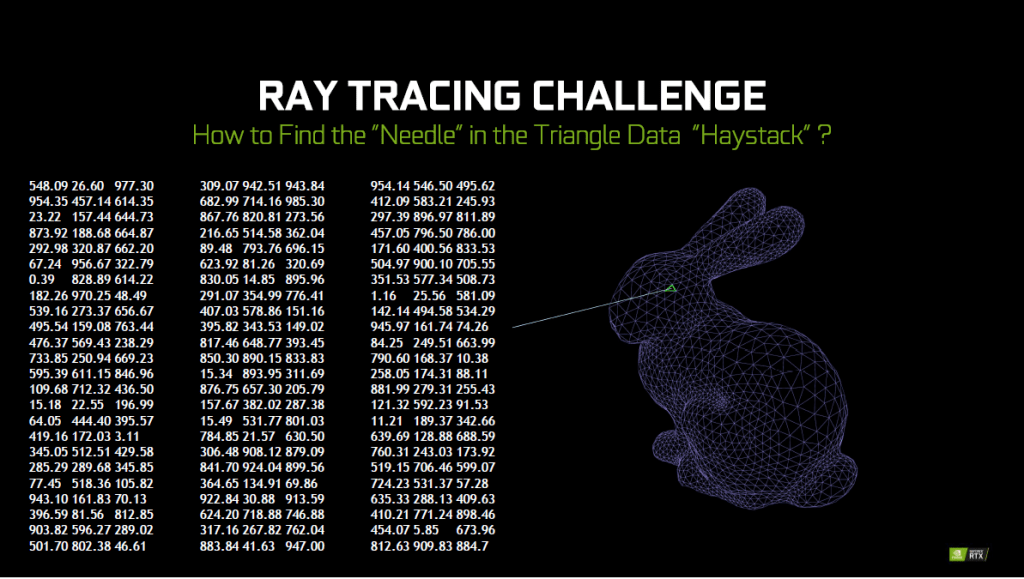
In order to ray trace an object, the light from the source of light is traced back to the camera. To do so, the specific point on the object have to be determine. From there, depending on the type of material and surface of the object, the amount of light that bounces off will vary. To find the specific point on the object, a lot of effort is needed to determine it. The combination of these steps results in a lot of time and computational power required to achieve a ray traced scene.
Bounding Volume Hierarchy (BVH) Algorithm
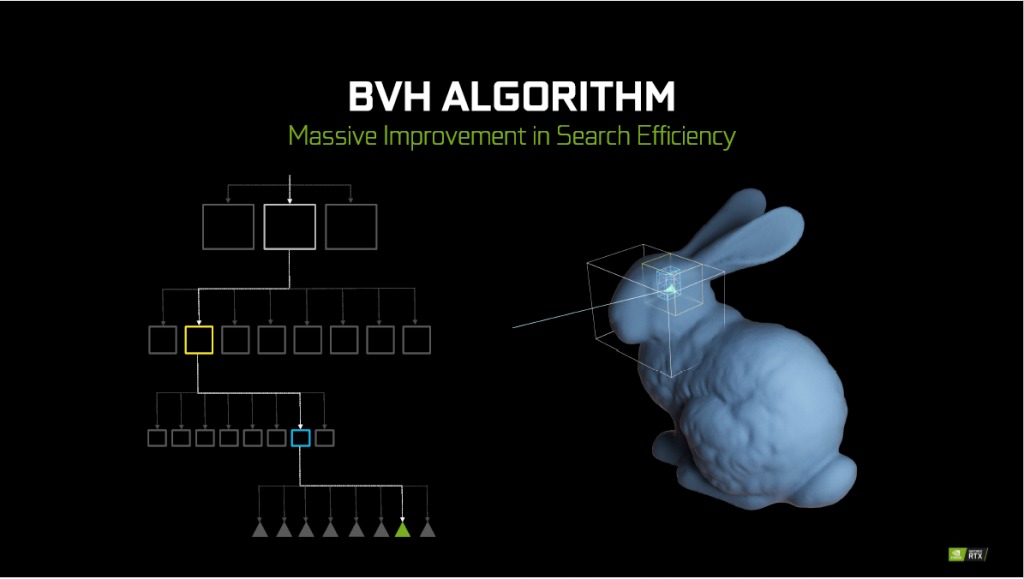
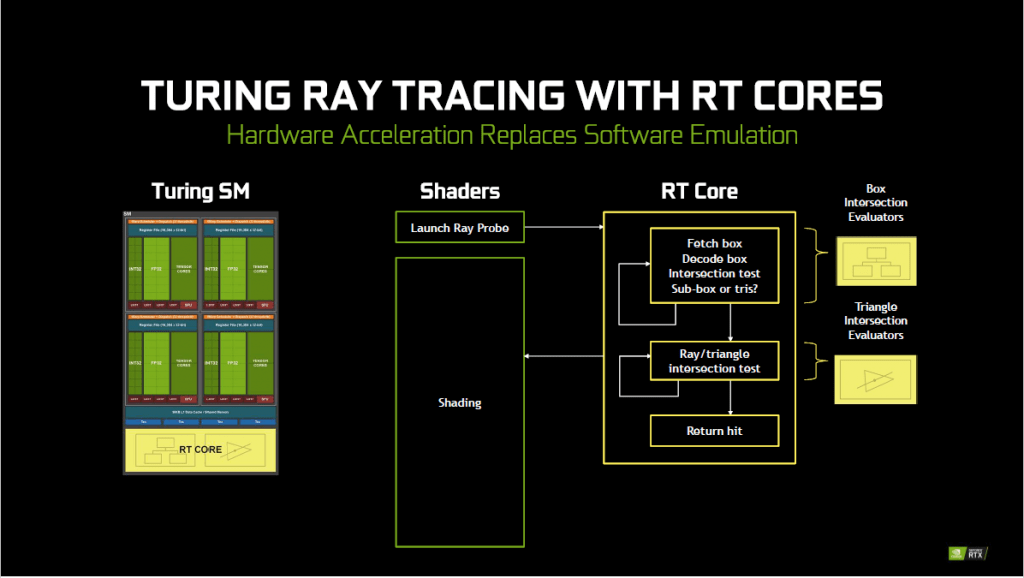
NVIDIA RTX implements the BVH algorithm to help reduce the effort needed to ray trace an object. BVH helps locate the region where the light intercept efficiently. Together with Hardware Acceleration with RT Cores, RTX is able to achieve real time ray tracing with relatively high frame rate. With 68 RT Cores, RTX 2080 Ti is able to achieve 10+ Giga Rays and is 10x faster than GTX 1080 Ti.
Advanced Graphics
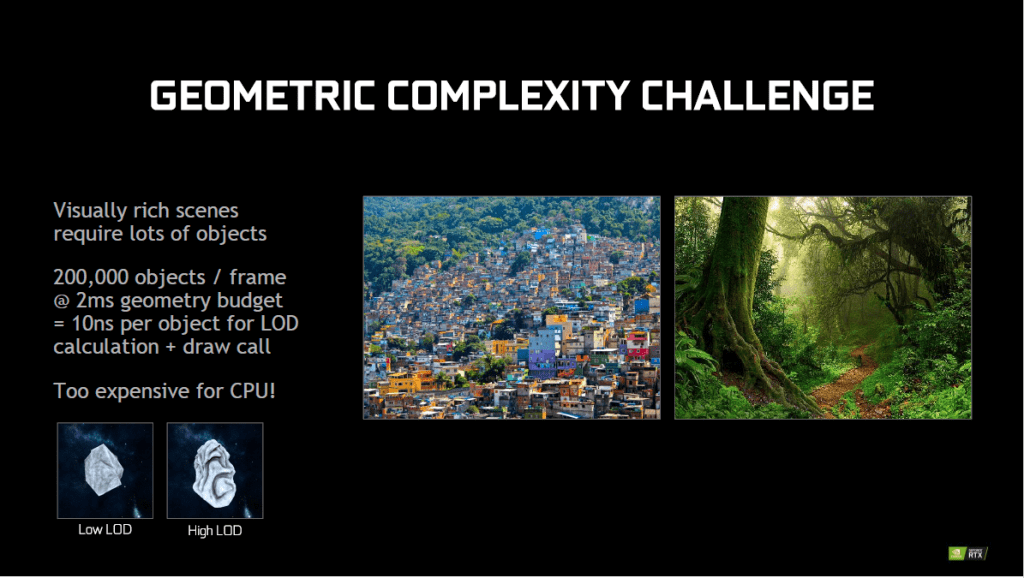
To produce a realistic scene, proper shading has to be done on object. Depending on where the object appears in a scene, different level of shading is required. In a visually rich scene with a lot of objects, it is computationally expensive for the CPU to render the various levels of shading. NVIDIA RTX is able to achieve a lower overhead through the use of Mesh Shaders and Variable Rate Shading.
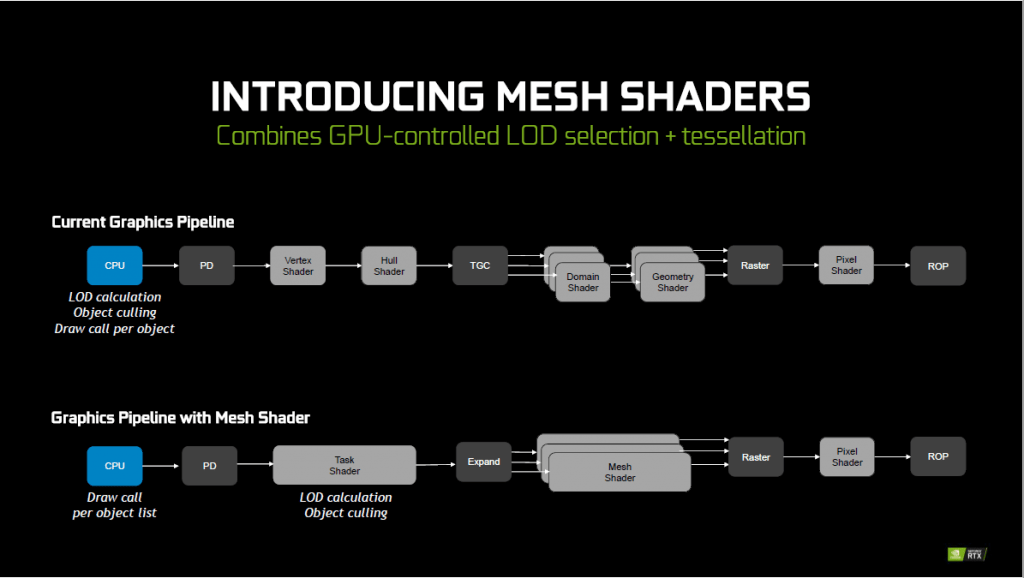
Mesh Shading manipulates the level of detail per object based on the distance of the object from the camera in a scene. This reduces overhead by shading the different level of segments based on the distance of the object from the camera in the scene. With this the level of details are preserved while achieving better performance.
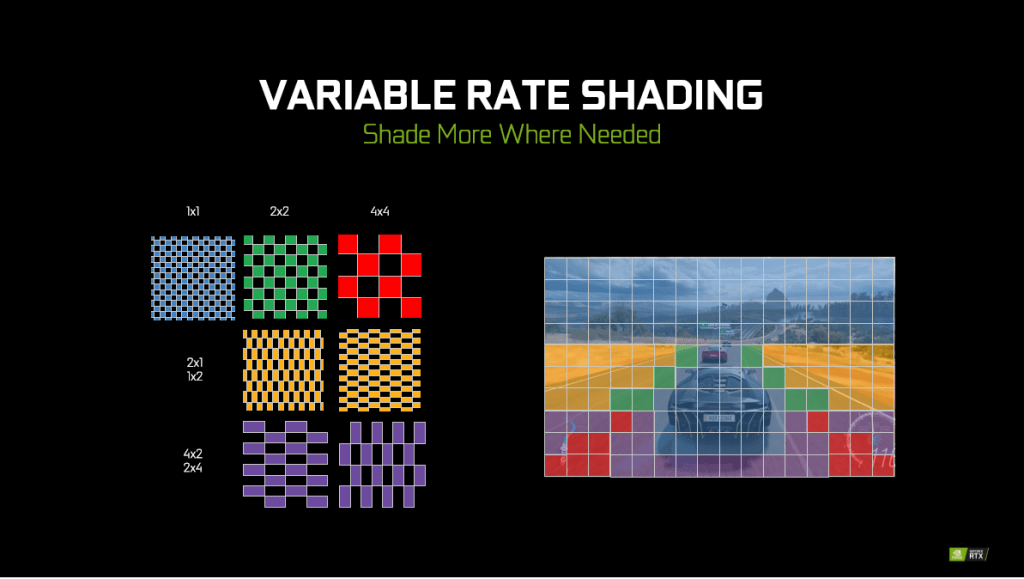

Variable Rate Shading is another similar approach as Mesh Shading that determines the different segments that requires various level of shading. Some of these segments just require more shading than the rest. Variable Rate Shading has many other uses as well, from Content Adaptive Shading to Lens Optimized Shading.
Tackling the Biggest Challenge

The many new features make available with the new Turing architecture have helped to overcome many challenges. Some of the challenges are in Virtual Reality, where it is not easy to achieve visual quality and many others. The future of gaming is bright with these improvements that NVIDIA has laid out for us.
Purchase Information
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2070 (Available in October 2018)
- MSRP – $499
- Founders Edition – $599
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080
- MSRP – $699
- Founders Edition – $799
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti
- MSRP – $999
- Founders Edition – $1,199