Technology to Partition, Visualize Complex Business Application Structures by
Function
operations, business changes
Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced that it has developed technology that
by analyzing a program can partition internal structures so as to simplify
modification of complex business applications.
Conventionally, business applications that
repeat revisions due to maintenance or the addition of new features often have
internal structures that become complex, and any modifications can have
wide-ranging ramifications. As a result, modifying applications in response to
business changes is an enormous burden.
In order to partition a business application
into each of its functional components, Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed
technology that analyzes the dependencies between programs and data, and then
identifies boundary candidates that would partition the program in a way that
decreases the mutual dependency. Using access logs to the database when the
application is actually run, Fujitsu Laboratories also developed technology
that, from among the boundary candidates, finds an area of the program that
should be executed as a series of operations, and then finds those areas where
the business relationship is highest. By enabling the visualization of the
program’s boundaries that partition by function, it is possible to partition
applications in cases that this had previously been difficult to achieve.
As a result, by adding revisions or upgrades
that localize the changes based on the boundaries, it makes it possible for
customers to quickly respond to changes in their operations or business.
Development Background
In the digital transformation of business using
ICT, there is now a need for technology that facilitates rapid modification of
existing business applications. In the manufacturing or retailing and
distribution industries, for example, it is frequently the case that new
locations are added or that there are changes in business partners, and when
these changes occur, there is also a need to change the business applications
themselves. Up until now, however, it was often the case that the structure of
business applications was complex and changes had far-ranging impact, which
required significant man hours of time consuming revisions. To resolve this
problem, as a method of designing applications in which business processes can be
quickly changed, in recent years there has been considerable interest in
microservices(1), which are structured as multiple services, each of which runs
independently. When parts of a program that frequently change are structured to
be independent, as is the case with microservices, it makes it easy to deal
with changes simply by replacing the services affected.
Issues
For applications that have undergone repeated
rounds of maintenance and feature additions, the program dependencies and the
data dependencies become quite complex, and it is frequently the case that
parts of the program can be affected that were not even envisioned in the
original design, making it difficult to partition existing applications into a
structure in which there are few dependencies. As a result, when trying to
partition a program to localize the affected areas, it was necessary to make
revisions while investigating many dependencies.
The Newly Developed Technology
Fujitsu Laboratories has now developed
technology to automatically identify boundaries that can partition the internal
structure of business applications by function, using the program source code
and database access logs as inputs.
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuFlowchartFig1.jpg
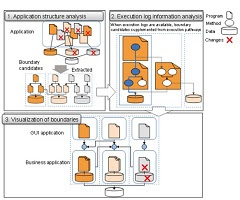
Figure 1: Flowchart for the newly developed
technology as a whole
This process of the technology is as follows.
1. Application structure analysis
When partitioning an application, this
technology analyses the structure of the application, arranging the data in a
way that minimizes the number of dependencies, and, in particular, extracts
boundaries that minimize mutual write operation dependencies.
Beginning with a program called from outside the
application, or a specified program, the technology defines groups that contain
all called functions. Then the program weights the relationships between them,
based on the idea that program groups that write to the same business data have
a deep relationship with business data, and extracts areas that are surrounded
by boundaries (Figure 1-1) using a clustering technology developed with Fujitsu
Laboratories’ proprietary application structure visualization software map
technology(2). At the same time, data that is written to by many program groups
is split off as common data.
2. Execution log information analysis
When database access logs collected when the
program actually runs are available for use, the technology identifies areas
where operations ought to be executed as a series, supplementing the results
obtained in the first step.
In analyzing execution log information, the
technology extracts database access commands as operational logs for the
business application being run, extrapolates data access commands that,
operationally ought to be executed in series, and identifies the programs
corresponding to those commands (Figure 1-2). Using this information, the
technology extracts areas of operations that ought to be executed as a series.
3. Visualization of boundaries
This technology uses software map technology to
visualize the results of the first two steps (Figure 1-3). The visualization
places areas with a strong mutual relationship close together.
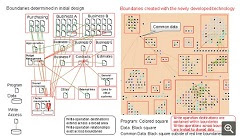
Effects
By using this technology to identify boundaries
with few dependencies, it has become possible to partition applications with a
reduced number of man-hours. For example, in a test using applications from a
purchasing department, the boundaries obtained from this newly developed
technology (Figure 2, right) reduced mutual dependencies to less than about 15%
compared with boundaries based on the categories established in the initial
design (Figure 2, left), which resulted in a reduced burden of investigation
and modification when partitioning the program.
Using these results, revisions and improvements
can be made to applications that localize the changes, while still considering
business relationships and update frequency, enabling rapid response to changes
in customers’ businesses. In addition, this technology enables customers to
more efficiently consider which parts of their business applications to shift
to microservices or migrate to the cloud in stages.
http://www.acnnewswire.com/topimg/Low_FujitsuFlowchartFig2.jpg
Figure 2: Example of boundary visualization
using categories based on the initial design (left) and the newly developed
technology (right)
Future Plans
Fujitsu Laboratories will continue to test the
application of this technology to the analyzing of business applications for a
variety of industries, with the goal of commercializing this technology in
fiscal 2018.
(1) Microservices
A method in which a service as a whole is not
developed as a single unit, but rather structured as multiple independent
services which operate while communicating in a lightweight format.
(2) Software map
This technology has already been incorporated
into application asset analysis services offered by Fujitsu Limited.
“Fujitsu Develops World’s First Software Map Generating Technology to
Leverage Application Portfolios,”.
For the LATEST tech updates,
FOLLOW us on our Twitter
LIKE us on our FaceBook
SUBSCRIBE to us on our YouTube Channel!