Intel’s Innovation 2023 tech showcase recently wrapped up, and here’s a brief overview of the key highlights that are more or less affecting normal consumers like you and me.
Advancements in Packaging and Multi-Chiplet Solutions
Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger kicked off the event with updates on their manufacturing processes – Intel 7 is now in high-volume production, Intel 4 is ready for production, and Intel 3 is slated for release by the end of 2023.
Additionally, Intel made a significant breakthrough by utilizing glass substrates, which they believe will allow Moore’s Law to extend beyond 2030, enabling the scaling of more transistors within packages without a complete overhaul of the basic understanding of chip fabrication.
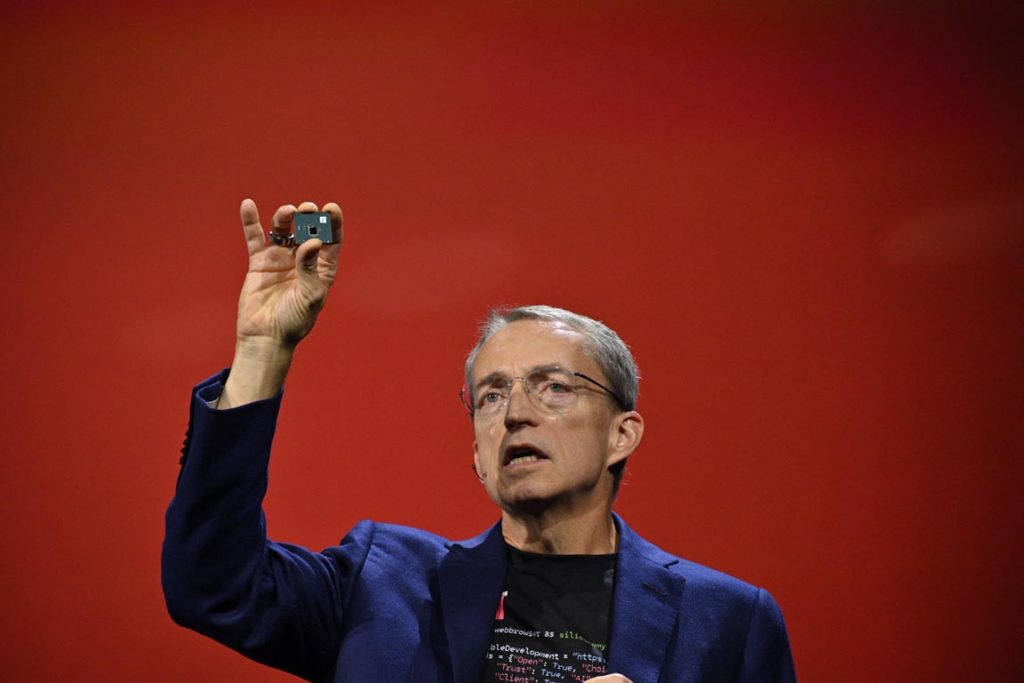

In the realm of multi-chipset solutions, they unveiled a test package utilizing Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe). UCIe aims to promote wide adoption through open standards, facilitating the integration of chips from various vendors to support diverse AI workloads.
The Mighty 288-core 5th Gen Xeon CPU
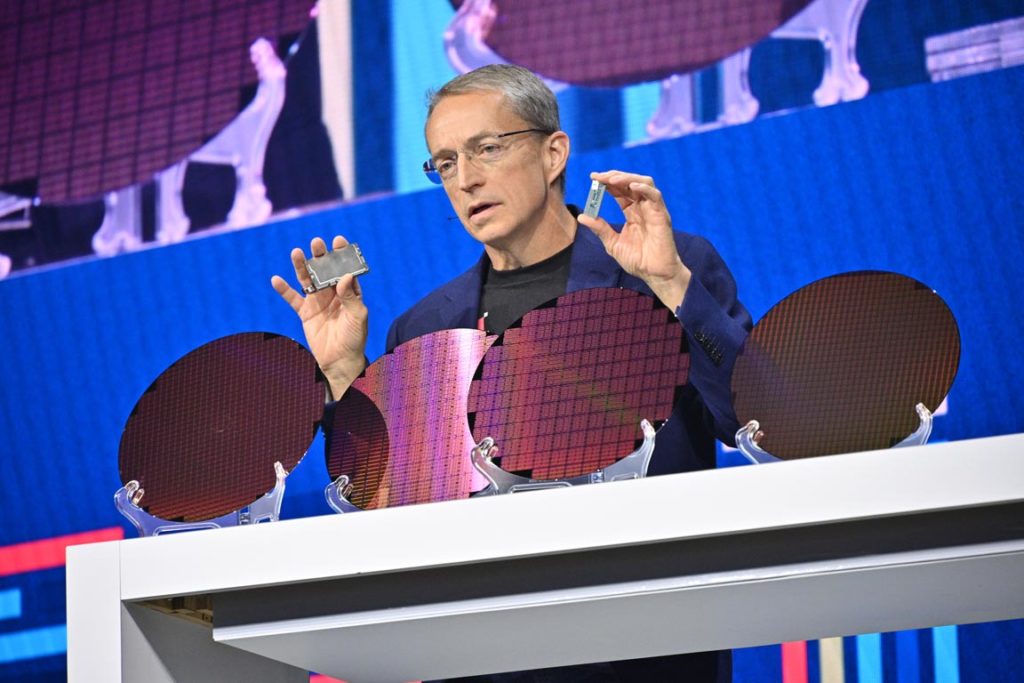

To start off the big movements in server-class computing, Team Blue revealed the upcoming groundbreaking AI supercomputer powered exclusively by Xeon processors and 4,000 Gaudi2 AI hardware accelerators.
And it will most likely carry the soon-to-be-released 5th Gen Intel Xeon processors and one of them showcased over there is the “Sierra Forest” E-core focused chips.
They are expected to deliver 2.5 times better rack density and 2.4 times higher performance per watt compared to the 4th Gen Xeon, boasting up to 288 cores.
On the other hand, Granite Rapids, the P-Core counterpart to Sierra Forest, is positioned for impressive AI performance gains, estimated at 2 to 3 times better than the previous generation is on track for next year.
2025 will see the Intel 18A-manufactured E-Core Xeon “Clearwater Forest” for now that’s all that is to know.
Intel Core Rebrand with Added AI Enhancements
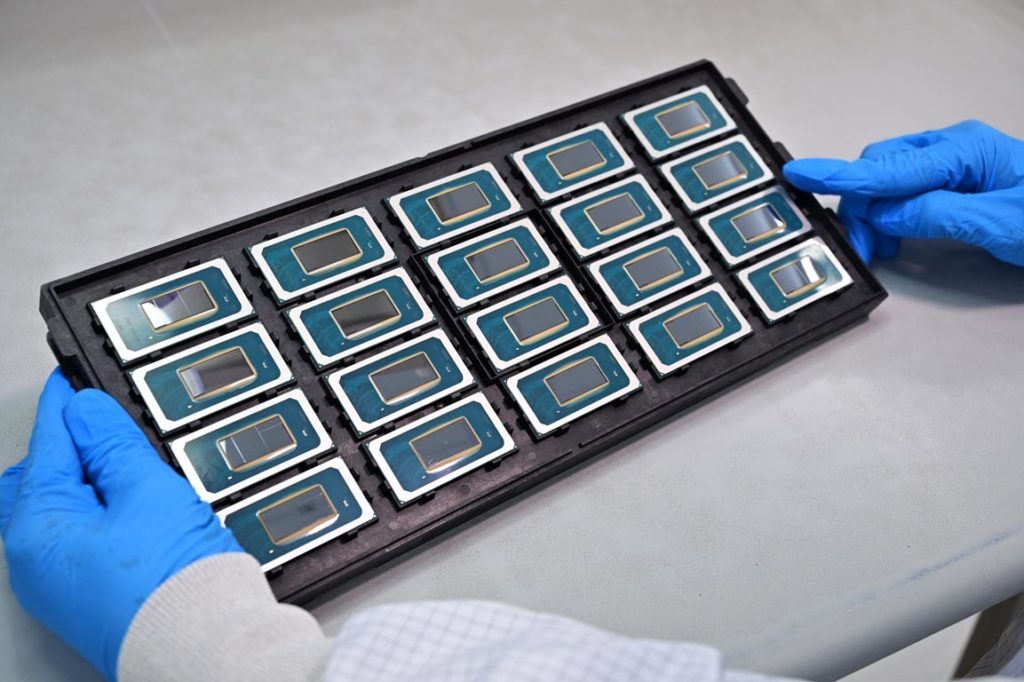

Intel is simplifying its Core CPU lineup by dropping the “i” designation, opting for “Core” and “Core Ultra” instead. Previously we assumed that Core Ultra would at most group unlockable chips, but there’s more to it.
The 14th Gen Intel Core Processors codenamed “Meteor Lake,” will incorporate an integrated neural processing unit (NPU) for efficient AI acceleration and local inferencing on standard consumer-grade PCs.
Chips using the Foveros packaging technology will launch on December 14, with desktop counterparts arriving next year (Meteor Lake is the mobile processor by the way).
Other Notable Updates
Here’s a quick bullet-point summary of other noteworthy developments that may or may not catch the attention of the average IT consumer:
- Intel Developer Cloud is now available for all clients, offering access to the latest computing hardware in cloud computing packages.
- OpenVINO, the in-house AI inferencing and deployment runtime, has been updated and released on OpenVINO.ai. This update allows developers to optimize standard PyTorch, TensorFlow, or ONNX models with improved model compression, enhanced GPU support, lower memory consumption, and full compatibility with the upcoming Meteor Lake Core Ultra CPUs.
- The introduction of Intel Trust Authority, a new service in the software security portfolio, provides unified yet independent assessments of trusted execution environment integrity and policy enforcement. It’s available for various platforms, including multi-cloud, hybrid, on-premises, and edge environments, as long as Intel confidential computing is deployed for secure AI computing.
- Collaboration with software vendors Red Hat, Canonical, and SUSE to ensure that their offerings fully comply with and support the latest Intel architectures.
- Kubernetes now includes Auto Pilot functionality for pod resource rightsizing, enabling automatic and optimized capacity management.
- Intel Granulate adds autonomous orchestration capabilities for Databricks workloads, resulting in cost reduction and faster processing times without the need for code changes.
- Intel is in the early stages of planning an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) accelerator dedicated to processing encrypted data without decryption, ensuring highly secure computing.






