In fact, it is actually not easy to overclock the Ryzen 7 1800X. These processors are already at their prime condition and settings, and further increase in clock speed will affect the stability of the whole system. The overclocking headroom is limited mainly by the temperature of the CPU core, and the scaling of clock speed to voltage. The voltage applied across the CPU (VCORE) also increases the temperature of the CPU. With the temperature of CPU already reaching over 70 degree celsius without overclocking on max load, we are in fact limited to apply additional voltage on the CPU for higher overclocks.
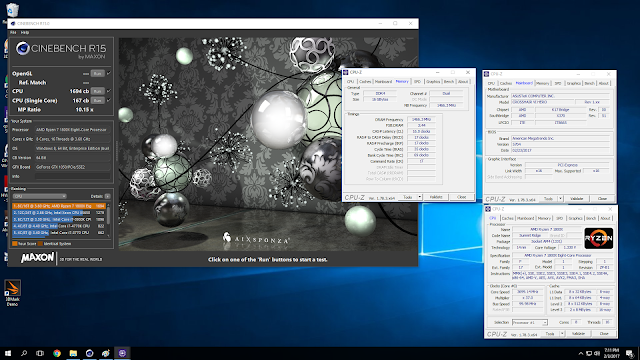 |
| Cinebench R15 on stock Ryzen 7 1800X |
Why can’t we attain the extended frequency range as stated by AMD with their (XFR) technology on an overclocked system? Essentially, with AMD’s XFR, only a certain number of cores will reach the additional boosted clock range to react to the rise in performance requirements. This allows the CPU to stay within its TDP and to complete the workload without any hiccups. When we apply overclock states to the CPU, we are in fact overclocking every single core of the CPU, setting them to run at the prescribed frequency. Thus, there is a higher voltage requirement to keep the whole CPU and all of its 8 cores stable.
Test Setup
- AMD Ryzen 7 1800X CPU @ Stock Settings
- ASUS Crosshair VI Hero Motherboard
- Cooler Master Master Liquid Pro 240
- Corsair Vengeance 3000MHz DDR4 2 x 8GB Kit (1.35V)
- ASUS NVIDIA GTX1050 Dual
- OCZ TL100 240GB SSD
- FSP HEXA+ 550W
- Windows 10 Enterprise 64Bit

 |
| Cinebench R15 on Ryzen 7 1800X @ 4.12GHz |
In our test, we managed to reach a clock speed of 4.125GHz. It is a small increase as compared to the stock XFR boost clock speed that is determined by AMD. However, since all the different CPU cores are running at such a speed, performance on multi threaded applications were extremely significant. In our Cinebench R15 test, we managed to squeeze out an additional 178cb points. Of course, in such a benchmark that utilizes all the threads on the CPU, an increase in clock speed will increase performance by the product of the number of cores and threads on the CPU. This is also why an overclock on the Ryzen 7 1800X will see an huge improvement in the Cinebench R15 test.
Do note that we instead of the 41x multiplier on a 100.6 reference clock, we dropped the multipler to 40.5x and increased the reference clock to 101.8. This allows us to increase our DRAM speed from 2933MHz to 2986MHz instead. Of course, the increase of improvement is still largely due to the CPU’s clock speed, and not the increase of DRAM frequency.
We simply can’t get past 4.125GHz. We were able to boot into Windows on 4.2GHz, but the system was unstable, and would not complete the benchmark. All changes to the settings of the CPU were done on the BIOS.
Perhaps, we could possibly try overclocking on Dry Ice / LN2 to really see how far this motherboard and CPU can go. With newer BIOS firmware that will be out on the motherboard, we are sure that higher overclocks can be achieved.
Other Ryzen related topics that may interest you :
- Ryzen 7 1800X Temperatures – http://www.thetechrevolutionist.com/2017/03/does-amd-ryzen-7-1800x-run-hot-simple.html
- CPU Single Thread VS Multi Thread Performance Benchmark – http://www.thetechrevolutionist.com/2017/03/amd-ryzen-7-1800x-single-and-multi.html
- Ryzen 7 1800X Power Consumption – http://www.thetechrevolutionist.com/2017/03/how-much-electrical-power-does-amd.html
- Ryzen 7 1800X Overclocked to 4.12GHz – http://www.thetechrevolutionist.com/2017/03/ryzen-7-1800x-overclocked-to-412ghz-on.html
- Ryzen Official Press Release – http://www.thetechrevolutionist.com/2017/03/amd-ryzen-7-desktop-processors.html
For the LATEST tech updates,
FOLLOW us on our Twitter
LIKE us on our FaceBook
SUBSCRIBE to us on our YouTube Channel!






